webAI and MacStadium(link is external) announced a strategic partnership that will revolutionize the deployment of large-scale artificial intelligence models using Apple's cutting-edge silicon technology.
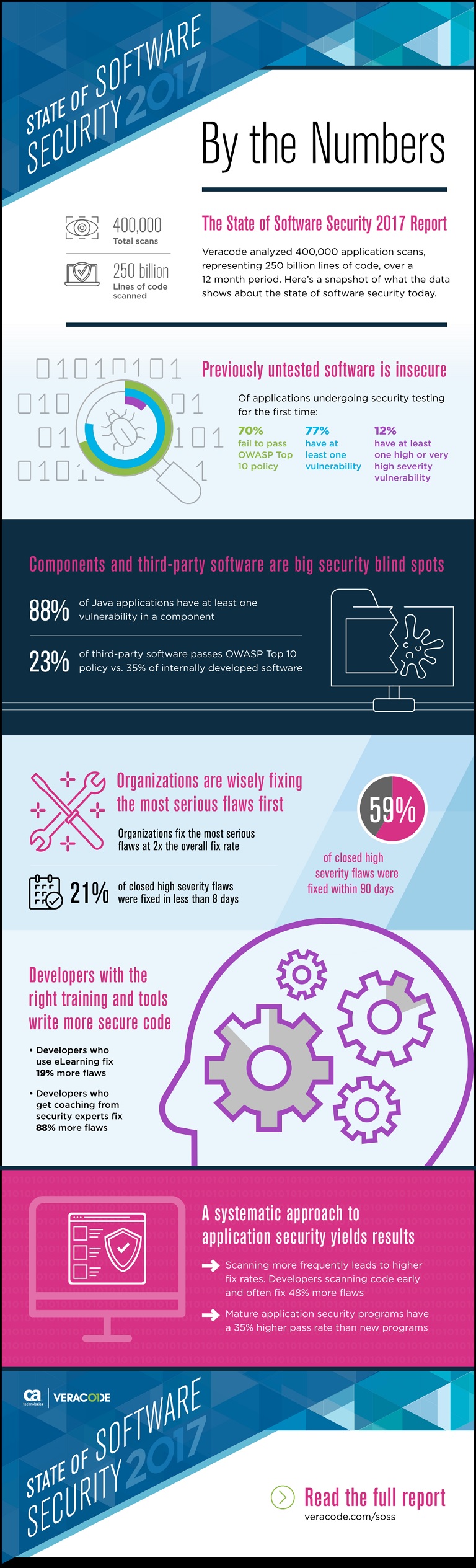
A new report by CA Veracode(link is external) found that 88 percent of Java applications contain at least one vulnerable component, making then susceptible to widespread attacks. This is in part because fewer than 28 percent of companies conduct regular composition analysis to understand which components are built into their applications.
“The universal use of components in application development means that when a single vulnerability in a single component is disclosed, that vulnerability now has the potential to impact thousands of applications – making many of them breachable with a single exploit,” said Chris Wysopal, CTO, CA Veracode.
Over the past 12 months, several high-profile breaches in Java applications were caused by widespread vulnerabilities in open source or commercial components. One example of a widespread component vulnerability was the “Struts-Shock” flaw disclosed in March 2017. According to the analysis, 68 percent of Java applications using the Apache Struts 2 library were using a vulnerable version of the component in the weeks following the initial attacks.
This critical vulnerability in the Apache Struts 2 library enabled remote code execution (RCE) attacks using command injection, for which as many as 35 million sites were vulnerable. Using this pervasive vulnerability, cybercriminals were able to exploit a range of victims’ applications, most notably the Canada Revenue Agency and the University of Delaware.
The 2017 State of Software Security Report also shows that approximately 53.3 percent of Java applications rely on a vulnerable version of the Commons Collections components. Even today, there are just as many applications using the vulnerable version as there were in 2016. The use of components in application development is common practice as it allows developers to reuse functional code – speeding up the delivery of software. Studies show that up to 75 percent of a typical application’s code is made up of open source components.
Wysopal continued, “development teams aren’t going to stop using components – nor should they. But when an exploit becomes available, time is of the essence. Open source and third party components aren’t necessarily less secure than code you develop in-house, but keeping an up-to-date inventory of what versions of a component you are using. We’ve now seen quite a few breaches as a result of vulnerable components and unless companies start taking this threat more seriously, and using tools to monitor component usage, I predict the problem will intensify.”
The report also shows that while many organizations prioritize fixing the most dangerous vulnerabilities, some still face challenges efficiently remediating software issues. Even the most severe flaws require significant time to fix (only 22 percent of very high severity flaws were patched in 30 days or less) and most attackers are leveraging vulnerabilities within days of discovery. Hackers and nation state organizations are given ample time to potentially infiltrate an enterprise network.
In addition to information regarding threat posed by the use of vulnerable components, the report also found:
■ Vulnerabilities continue to crop up in previously untested software at alarming rates. 77 percent of apps have at least one vulnerability on initial scan.
■ Government organizations continue to underperform those in other industries. Not only did they have a 24.7 percent pass rate at latest scan, they also had the highest prevalence of highly exploitable vulnerabilities like cross-site scripting (49 percent) and SQL injection (32 percent).
■ Comparatively, between first and last scan, critical infrastructure had the strongest OWASP pass rate (29.8 percent) across all industries studied, though it saw a slight decline in pass rate (29.5 percent) on last scan. Two industries showing slight improvements between first and last scan include healthcare (27.6 percent vs. 30.2 percent) and retail & hospitality (26.2 percent vs. 28.5 percent).
Methodology: Data for the eighth volume of CA Veracode’s 2017 State of Software Security Report is derived from scans conducted by CA Veracode’s base of 1,400+ customers, and was drawn from code-level analysis of nearly 250 billion lines of code, across 400,000 assessments performed during the 12 month period from April 1, 2016 to March 31, 2017. The findings are representative of the application security industry’s most comprehensive review of application testing data.
Industry News
Development work on the Linux kernel — the core software that underpins the open source Linux operating system — has a new infrastructure partner in Akamai. The company's cloud computing service and content delivery network (CDN) will support kernel.org, the main distribution system for Linux kernel source code and the primary coordination vehicle for its global developer network.
Komodor announced a new approach to full-cycle drift management for Kubernetes, with new capabilities to automate the detection, investigation, and remediation of configuration drift—the gradual divergence of Kubernetes clusters from their intended state—helping organizations enforce consistency across large-scale, multi-cluster environments.
Red Hat announced the latest updates to Red Hat AI, its portfolio of products and services designed to help accelerate the development and deployment of AI solutions across the hybrid cloud.
CloudCasa by Catalogic announced the availability of the latest version of its CloudCasa software.
BrowserStack announced the launch of Private Devices, expanding its enterprise portfolio to address the specialized testing needs of organizations with stringent security requirements.
Chainguard announced Chainguard Libraries, a catalog of guarded language libraries for Java built securely from source on SLSA L2 infrastructure.
Cloudelligent attained Amazon Web Services (AWS) DevOps Competency status.
Platform9 formally launched the Platform9 Partner Program.
Cosmonic announced the launch of Cosmonic Control, a control plane for managing distributed applications across any cloud, any Kubernetes, any edge, or on premise and self-hosted deployment.
Oracle announced the general availability of Oracle Exadata Database Service on Exascale Infrastructure on Oracle Database@Azure(link sends e-mail).
Perforce Software announced its acquisition of Snowtrack.
Mirantis and Gcore announced an agreement to facilitate the deployment of artificial intelligence (AI) workloads.
Amplitude announced the rollout of Session Replay Everywhere.
Oracle announced the availability of Java 24, the latest version of the programming language and development platform. Java 24 (Oracle JDK 24) delivers thousands of improvements to help developers maximize productivity and drive innovation. In addition, enhancements to the platform's performance, stability, and security help organizations accelerate their business growth ...