webAI and MacStadium(link is external) announced a strategic partnership that will revolutionize the deployment of large-scale artificial intelligence models using Apple's cutting-edge silicon technology.
From facial recognition to self-driving cars, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) have become commonplace for many industries in recent years. In parallel, the software development industry has undergone a transformation of its own.
As customers look to engage more through digital experiences, businesses have been forced to evolve faster than ever before. Enticing and delighting customers in every aspect of product delivery has become "business critical," determining if the customer chooses, and continues, to do business with you over a competitor. Although the discipline of Quality Engineering has remained unchanged, every aspect of how quality is delivered has evolved. Businesses can no longer trade off quality vs. speed, as both quality and speed must be achieved for modern digital-first businesses.
Recently, two reports came out that speak directly to the intersection of these two trends and discuss how industry leaders are leveraging AI to modernize their approach to Quality Engineering in 2021 and beyond.
The first, from EMA (Enterprise Management Associates), is titled Disrupting the Economics of Software Testing Through AI(link is external). In this report, author Torsten Volk, Managing Research Director at EMA, discusses the reasons why traditional approaches to software quality cannot scale to meet the needs of modern software delivery. He highlights 5 key categories of AI and 6 critical pain points of test automation that AI addresses.
In addition, over the last couple of months Sogeti has been releasing sections of their State of AI applied to Quality Engineering 2021-22 report(link is external) (with still more sections to come through February 2022). This comprehensive report is created in partnership with leading technology providers to provide a detailed examination of the current state of artificial intelligence across many use-cases in the field of Quality Engineering and centers around a key question — how can AI make quality validation smarter?
As the application of AI to testing continues to advance, it is important to understand its potential and how it can help improve the quality, velocity, and efficiency of Quality Engineering activities. Below, I’ll discuss some of the highlights from both of these reports and what they define as the future of Quality Engineering.
The Emergence of Modern Quality Engineering and the Need for AI
First, let’s talk about the reason why traditional approaches to software quality and test automation are no longer sufficient. The first section(link is external) of the Sogeti report gives an overview of the business pressure to release faster and increasingly complex technical environments. As Torsten discusses in his report, modern software development teams are faced with many challenges that have driven up the complexity and cost of quality, such as the explosion of device/browser combinations and application complexity. Multiply this by the number of releases per month and you can quickly see that the traditional test automation tools can no longer scale to the challenges of modern software delivery.

Source: Disrupting the Economics of Software Testing Through AI, September 2021, EMA Research
The biggest problem with the traditional approach to test automation is that it scales linearly. The more, or faster, you need to test the more human and non-human resources you need — which only works if you have an infinite amount of resources (do you?).
With this in mind, the EMA and Sogeti reports discuss the ways modern organizations can leverage AI/ML to streamline their test automation practices and scale to meet the increased pace of software delivery.
AI Scales Test Automation to Identify Issues Before They Impact Users
When it comes to Quality Engineering, certain tools are capable of controlling the graphical user interface (GUI) or an application programming interface (API). Others analyze coverage and recommend additional actions, and some analyze log files in search of specific behaviors. These are just a few examples. But to increase developer productivity, there needs to be an understanding of each of these tasks and how they can be optimized.
How does this relate to AI? AI has the ability to apply algorithms and approaches used in tools to perform human-like tasks. For example, a developer can reason by examining an application to determine whether or not it has been properly tested. If the testing cycle has fallen short, they can then determine what additional testing needs to be done. AI has the potential to act in a similar manner. Although AI may require some training, once it has been trained it has the potential to continue to test the function even as the application evolves.
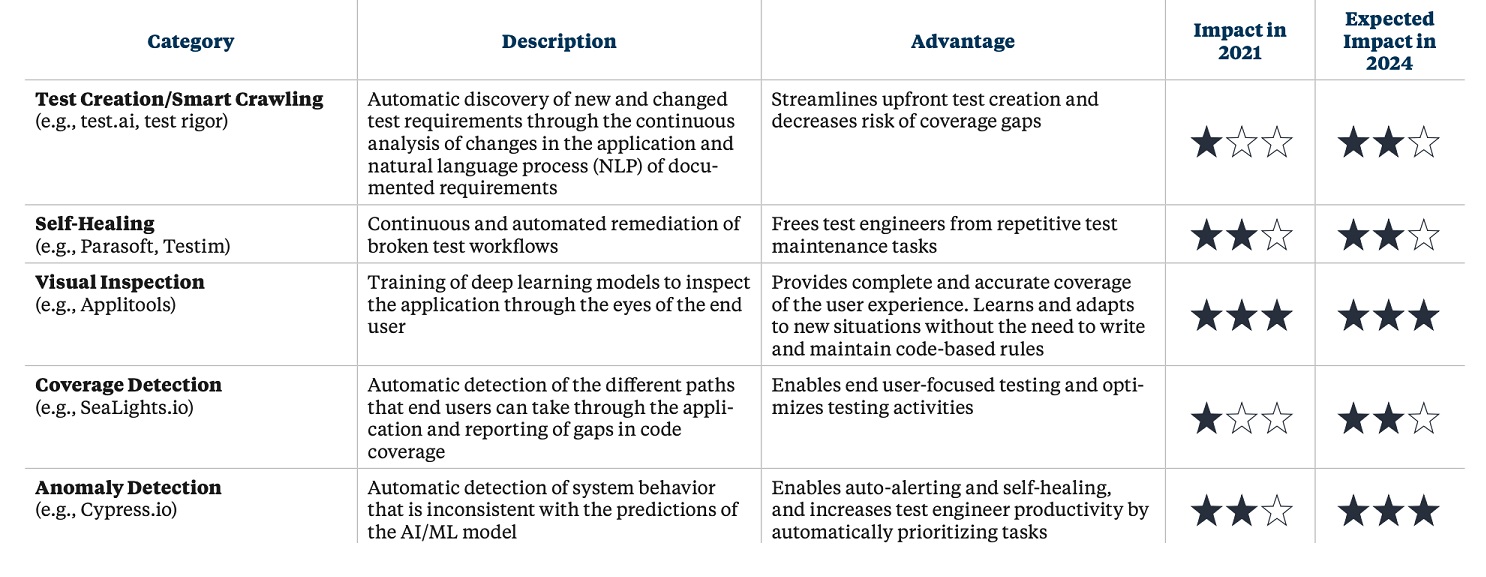
The EMA report details five key AI capabilities that can help organizations streamline and automate parts of their quality and testing workflow:
■ Test Creation/Smart Crawling: Automatic discovery of new and changed test requirements through the continuous analysis of changes in the application and natural language process (NLP) of documented requirements
■ Self-Healing: Continuous and automated remediation of broken test workflows
■ Visual Inspection: Training of deep learning models to inspect the application through the eyes of the end user
■ Coverage Detection: Automatic detection of the different paths that end users can take through the application and reporting of gaps in code coverage
■ : Automatic detection of system behavior that is inconsistent with the predictions of the AI/ML model
Source: Disrupting the Economics of Software Testing Through AI, September 2021, EMA Research
The report highlights the key advantage of each capability and then details how the capabilities can bridge the gap between the "ideal scenario" and "in real life" situation for six critical pain points of Test Automation: false positives, test maintenance, insufficient feedback, application complexity, device/use-case coverage and toolchain complexity.
Each capability is assigned a rating, ranking their current impact in 2021 and predicting their future impact in 2024. Visual inspection, implemented with Visual AI, has the highest rating for both current and future impact with the key advantage that it "Provides complete and accurate coverage of the user experience. It learns and adapts to new situations without the need to write and maintain code-based rules."
The EMA report goes on to add that "Smart crawling, self-healing, anomaly detection, and coverage detection each are point solutions that help organizations lower their risk of blind spots while decreasing human workload. Visual inspection (Visual AI) goes further compared to these point solutions by aiming to understand application workflows and business requirements."
As discussed in the most recent section of the Sogeti report, Shorten Release Cycles with Visual AI(link is external), Visual AI is already a mature technology, currently being adopted by leading brands across industries to accelerate the delivery of their digital experiences. The high levels of accuracy, and ability to handle dynamic and shifting content, ensures teams do not get overwhelmed with false positives. The automated grouping and categorization of regressions, coupled with root cause analysis, accelerates feedback and reduces test maintenance efforts. Visual AI provides test engineers with an additional "pair of eyes," leaving them to focus on areas that really need human intelligence — the power and impact of this approach is enormous.
From AI assistance to Autonomous Testing
Currently the industry is focused on having AI remove repetitive and mundane tasks, freeing humans to focus on the creative/complex tasks that require human intelligence. And as Torsten mentions in his report, "AI-based test automation technologies can deliver real ROI today and have the potential to address, and ultimately eliminate, today’s critical automation bottlenecks."
The ROI will further increase as we look to the future and the next big innovation for Quality Engineering, Autonomous Testing. Autonomous Testing will change the role of developers and testers from testing the application to training the AI how to use the application, leaving it to perform the testing activities, and then reviewing the results. This change will deliver a fundamental increase in team efficiency, reducing the overall cost of quality and enabling businesses to establish truly scalable Quality Engineering practices.
Industry News
Development work on the Linux kernel — the core software that underpins the open source Linux operating system — has a new infrastructure partner in Akamai. The company's cloud computing service and content delivery network (CDN) will support kernel.org, the main distribution system for Linux kernel source code and the primary coordination vehicle for its global developer network.
Komodor announced a new approach to full-cycle drift management for Kubernetes, with new capabilities to automate the detection, investigation, and remediation of configuration drift—the gradual divergence of Kubernetes clusters from their intended state—helping organizations enforce consistency across large-scale, multi-cluster environments.
Red Hat announced the latest updates to Red Hat AI, its portfolio of products and services designed to help accelerate the development and deployment of AI solutions across the hybrid cloud.
CloudCasa by Catalogic announced the availability of the latest version of its CloudCasa software.
BrowserStack announced the launch of Private Devices, expanding its enterprise portfolio to address the specialized testing needs of organizations with stringent security requirements.
Chainguard announced Chainguard Libraries, a catalog of guarded language libraries for Java built securely from source on SLSA L2 infrastructure.
Cloudelligent attained Amazon Web Services (AWS) DevOps Competency status.
Platform9 formally launched the Platform9 Partner Program.
Cosmonic announced the launch of Cosmonic Control, a control plane for managing distributed applications across any cloud, any Kubernetes, any edge, or on premise and self-hosted deployment.
Oracle announced the general availability of Oracle Exadata Database Service on Exascale Infrastructure on Oracle Database@Azure(link sends e-mail).
Perforce Software announced its acquisition of Snowtrack.
Mirantis and Gcore announced an agreement to facilitate the deployment of artificial intelligence (AI) workloads.
Amplitude announced the rollout of Session Replay Everywhere.
Oracle announced the availability of Java 24, the latest version of the programming language and development platform. Java 24 (Oracle JDK 24) delivers thousands of improvements to help developers maximize productivity and drive innovation. In addition, enhancements to the platform's performance, stability, and security help organizations accelerate their business growth ...






