webAI and MacStadium(link is external) announced a strategic partnership that will revolutionize the deployment of large-scale artificial intelligence models using Apple's cutting-edge silicon technology.
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are incredibly important in today's digital landscape. They play a crucial role in enabling communication and interaction between different software applications, systems, and services. Due to the increasing reliance on APIs, they have gradually become the top target for hackers. As such, enterprises are placing more emphasis on API security to protect the integrity of data and services, build trust and confidence, and mitigate future risks.
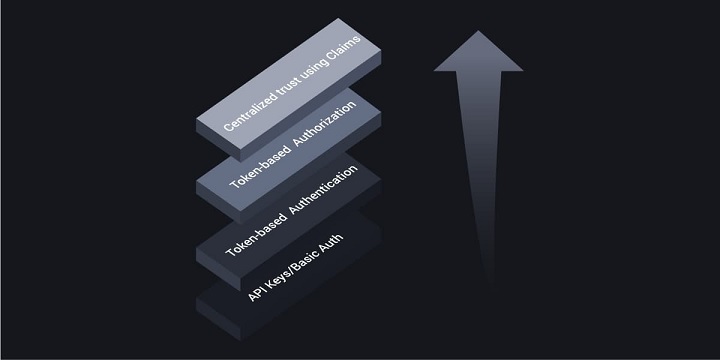
This blog will explore the different levels of API security by examining the API Security Maturity Model, a framework in which security and trust increase according to each level. The higher up on the model, the better organizations are equipped to protect their systems more efficiently.
The API Security Maturity Model is divided into four layers:
Level 0: API Keys and Basic Authentication
Level 1: Token-Based Authentication
Level 2: Token-Based Authorization
Level 3: Centralized Trust Using Claims
Level 0: API Keys and Basic Authentication
API keys and basic authentication, common methods for API security, are considered level 0. Both of these methods provide authentication to protect API resources. However, API keys can easily be compromised as they can only verify from machine to machine without considering the user's identity. In many cases, API keys are not renewed, so an attacker can use them maliciously for a long time.
In addition, API keys and basic authentication don't cover the authorization process. Authorization is vital as it helps determine the actions the user can perform within a system and whether they have permission to access certain resources or data.

Level 1: Token-Based Authentication
Token-based authentication is a user authentication method commonly used in web applications and APIs. Instead of using traditional username and password credentials, token-based authentication relies on access tokens to authenticate users and grant them access to protected resources. However, anyone with the access token can modify the API and gain access to the protected resources, as authorization is still not part of the process.
Level 2: Token-Based Authorization
In level 2 of the API Security Maturity Model, a token-based architecture is used for authorization. Token-based authorization is a method of controlling access to resources in web applications and APIs based on the presence and validity of a token. This token is generated during the authentication process and contains information about the user's identity and permissions.
APIs in level 2 use OAuth 2.0, an industry-standard authentication and authorization protocol used to grant third-party applications limited access to user resources on a web service without requiring the user to share their login credentials directly with the application. One of the advantages of OAuth is Scopes. Scopes enable access tokens issued to clients to use only restricted privileges.
The main issue with level 2 is that not all values used for API authorization are supplied securely. Even though a token is used to access a user's resources, other values may be passed in plain HTTP headers or URL path segments. A malicious party could potentially alter these values to elevate their privileges.
Level 3: Centralized Trust Using Claims
Level 3 is the most advanced tier of the API Security Maturity model, thus providing the highest level of security for your APIs. At this level, the API receives all secure values in access tokens delivered in a JSON web token (JWT) format. If these values are altered, the JWT will fail cryptographic validation. Such values are called claims and might include a user ID, company ID, and roles. Claims aid in the authorization or authentication of a user by providing more contextual information regarding the issued token and who the issuer is. Claims help to build an identity-based API security system that validates the identity of the user and their level of access to applications, resources, or services.
Conclusion
It is now more critical than ever for enterprises to adopt robust API security practices to protect their resources and users. The API security maturity model delineates the different levels of API security from very basic to advanced implementations. As explained, API keys are not adequate to secure modern APIs. An identity-centric approach based on claims is required to ensure the highest level of authentication and authorization of the user.
Industry News
Development work on the Linux kernel — the core software that underpins the open source Linux operating system — has a new infrastructure partner in Akamai. The company's cloud computing service and content delivery network (CDN) will support kernel.org, the main distribution system for Linux kernel source code and the primary coordination vehicle for its global developer network.
Komodor announced a new approach to full-cycle drift management for Kubernetes, with new capabilities to automate the detection, investigation, and remediation of configuration drift—the gradual divergence of Kubernetes clusters from their intended state—helping organizations enforce consistency across large-scale, multi-cluster environments.
Red Hat announced the latest updates to Red Hat AI, its portfolio of products and services designed to help accelerate the development and deployment of AI solutions across the hybrid cloud.
CloudCasa by Catalogic announced the availability of the latest version of its CloudCasa software.
BrowserStack announced the launch of Private Devices, expanding its enterprise portfolio to address the specialized testing needs of organizations with stringent security requirements.
Chainguard announced Chainguard Libraries, a catalog of guarded language libraries for Java built securely from source on SLSA L2 infrastructure.
Cloudelligent attained Amazon Web Services (AWS) DevOps Competency status.
Platform9 formally launched the Platform9 Partner Program.
Cosmonic announced the launch of Cosmonic Control, a control plane for managing distributed applications across any cloud, any Kubernetes, any edge, or on premise and self-hosted deployment.
Oracle announced the general availability of Oracle Exadata Database Service on Exascale Infrastructure on Oracle Database@Azure(link sends e-mail).
Perforce Software announced its acquisition of Snowtrack.
Mirantis and Gcore announced an agreement to facilitate the deployment of artificial intelligence (AI) workloads.
Amplitude announced the rollout of Session Replay Everywhere.
Oracle announced the availability of Java 24, the latest version of the programming language and development platform. Java 24 (Oracle JDK 24) delivers thousands of improvements to help developers maximize productivity and drive innovation. In addition, enhancements to the platform's performance, stability, and security help organizations accelerate their business growth ...




