Check Point® Software Technologies Ltd.(link is external) announced that it has ranked as a Leader and the only Outperformer for its Check Point Quantum(link is external) Security Solutions in GigaOm’s latest Radar for Enterprise Firewall report(link is external).
Managing and securing your software supply chain is vital to delivering reliable, trusted releases in today's software world. With the constant growth of open-source components, assessing your organization's ability to manage them is crucial.
To help you prepare, JFrog compiled a report that combines the company's usage data, CVE analysis conducted by the JFrog Security Research Team, and commissioned third-party polling data from 1,224 professionals in security, development, and operations roles. Below is an overview of some key findings that we discovered.
Four of the report's most crucial themes include:
■ The software supply chain is growing rapidly: The open-source ecosystem is quickly expanding, leading to a vast software supply chain.
■ Understanding risk is key. Not all reported vulnerabilities require immediate attention, so focusing on where the real risks lie is essential.
■ Where security efforts should be focused: There's a growing awareness of security, but disjointed approaches cost development teams approximately a quarter of their monthly working time.
■ The impact of AI and ML: Organizations must be deliberate about leveraging AI-based tools and quickly adopt security best practices for model use.
The rapid expansion of tools, technologies, and programming languages in today's landscape presents a significant challenge for organizations and could place considerable pressure on their operations.
According to the report:
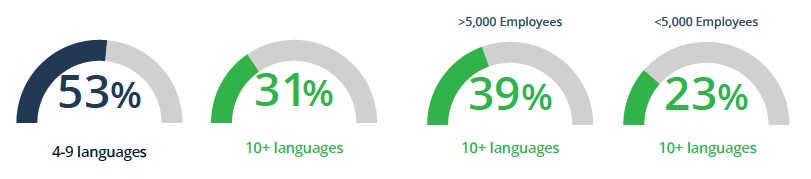
How many programming languages do you use in your software development organization? (Commissioned survey, 2023)
Over half of organizations (53%) utilize four to nine programming languages, while 31% use more than 10 languages. Predictably, the larger the organization, the more programming languages are likely used.
And while there are dozens of programming languages and packaging technologies to choose from when building production-ready applications, JFrog data shows that traditional, tried and true technologies are still the most popular — npm (Javascript), Maven (Java), Docker, PyPI (Python), Go, Nuget (.NET), and Conan (C/C++).
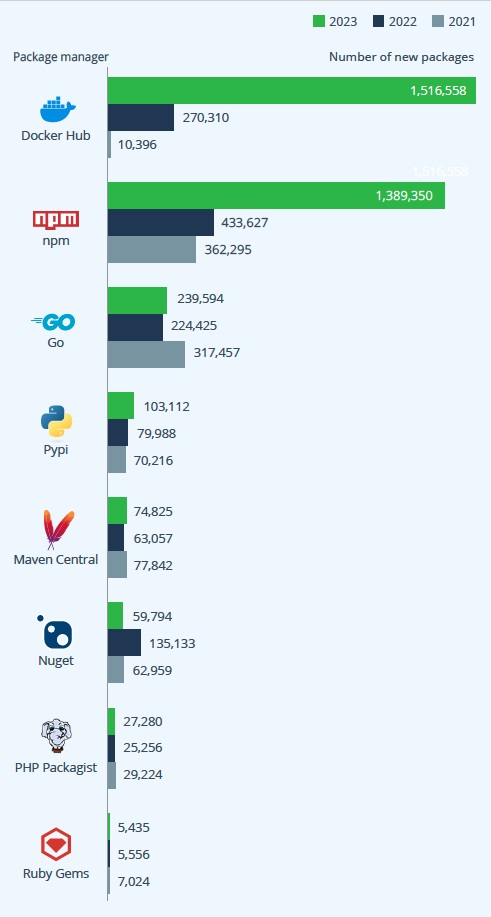
Number of new packages per year, displayed by package type (JFrog Catalog data, 2023)
For their chosen technologies, organizations have to sift through more and more open source packages to find the ones best suited for their projects. Docker and npm are the package types that have contributed the most by far. PyPI's contribution is also on the rise, likely driven by AI/ML use cases.
The variety of available open-source packages and libraries is thriving, but as the report explores, it inadvertently creates a world of potential risk for organizations. In 2023, over 26,000 new CVEs (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) were introduced to the open source ecosystem, continuing the upward trend YoY.
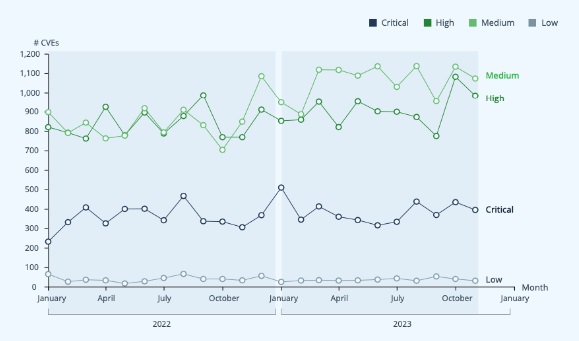
CVEs by month and severity in the last 2 years (National Vulnerability Database analyzed by JFrog Security Research)
An examination of CVEs recorded in the National Vulnerability Database from January 2022 to November 2023 reveals the consistent presence of Critical and Low CVEs, while medium and High CVEs show a notable upward trend. While this trend may raise concerns, an analysis of more than 200 high-profile CVEs in 2023 conducted by the JFrog Security Research team presents a contrasting narrative. The JFrog Security Research Team downgraded 85% of Critical CVEs and 73% of High CVEs it examined.
Vulnerabilities in Open Source components aren't the only source of risk organizations must manage. Human error also creates risk and has been the cause of some of the biggest security events of the past year. Take, for example, exposed secrets (ie. tokens) accidentally left in code. After examining common open-source software registries, including npm, PyPI, RubyGems, crates.io and DockerHub, the JFrog Security Research Team identified over 15,000 tokens. This is less than compared to 2022, but still an alarming number.
Organizations have a varied approach to tackling risk in their software supply chain — from where they scan and the different tools that they use. A third of respondents indicated their organization uses 10 or more application security tools, with nearly half using 4-9. The challenge is that security activities are taking up a significant amount of time — roughly 4 working days in a given month — that could be used to deliver new value to customers.
Looking forward, there will always be risk in software development and the growing complexity of the software supply chain will only make it more difficult to manage. However, with the right tools and practices, organizations can continue to drive software innovation and ensure that trusted, quality software is released to customers.
Industry News
Postman announced new releases designed to help organizations build APIs faster, more securely, and with less friction.
SnapLogic announced AgentCreator 3.0, an evolution in agentic AI technology that eliminates the complexity of enterprise AI adoption.
GitLab announced the general availability of GitLab Duo with Amazon Q.
Perforce Software and Liquibase announced a strategic partnership to enhance secure and compliant database change management for DevOps teams.
Spacelift announced the launch of Saturnhead AI — an enterprise-grade AI assistant that slashes DevOps troubleshooting time by transforming complex infrastructure logs into clear, actionable explanations.
CodeSecure and FOSSA announced a strategic partnership and native product integration that enables organizations to eliminate security blindspots associated with both third party and open source code.
Bauplan, a Python-first serverless data platform that transforms complex infrastructure processes into a few lines of code over data lakes, announced its launch with $7.5 million in seed funding.
Perforce Software announced the launch of the Kafka Service Bundle, a new offering that provides enterprises with managed open source Apache Kafka at a fraction of the cost of traditional managed providers.
LambdaTest announced the launch of the HyperExecute MCP Server, an enhancement to its AI-native test orchestration platform, HyperExecute.
Cloudflare announced Workers VPC and Workers VPC Private Link, new solutions that enable developers to build secure, global cross-cloud applications on Cloudflare Workers.
Nutrient announced a significant expansion of its cloud-based services, as well as a series of updates to its SDK products, aimed at enhancing the developer experience by allowing developers to build, scale, and innovate with less friction.
Check Point® Software Technologies Ltd.(link is external) announced that its Infinity Platform has been named the top-ranked AI-powered cyber security platform in the 2025 Miercom Assessment.
Orca Security announced the Orca Bitbucket App, a cloud-native seamless integration for scanning Bitbucket Repositories.
The Live API for Gemini models is now in Preview, enabling developers to start building and testing more robust, scalable applications with significantly higher rate limits.




