MacStadium(link is external) announced the extended availability of Orka(link is external) Cluster 3.2, establishing the market’s first enterprise-grade macOS virtualization solution available across multiple deployment options.
There might be many people across organizations who claim that they’re using a DevOps approach, but often times, the “best practices” they’re using don’t align with DevOps methodologies. They can say what they do is “DevOps”, but what we’ve found is that many are actually not following basic agile methodology principles, and that’s not DevOps. Ever.
How Are We So Sure?
Electric Cloud gathered data from thousands of engineers and IT leaders across three major events – DOES 2016, Agile 2016 and Appshere 2016 (and compared it with specific data sets from the Puppet and DORA 2016 State of the DevOps Report) – asking them about their deployment and application release automation practices, and we found some interesting patterns.
For starters, the data show us that the majority of deployments are still manual. Specifically, over 70 percent of deployments use a combination of manual processes and some automation. While many think, in this instance, that they are automating their releases, this isn’t automation. Just because you’re using a Chef recipe to automate one of your releases, doesn’t mean you’re an automated shop.
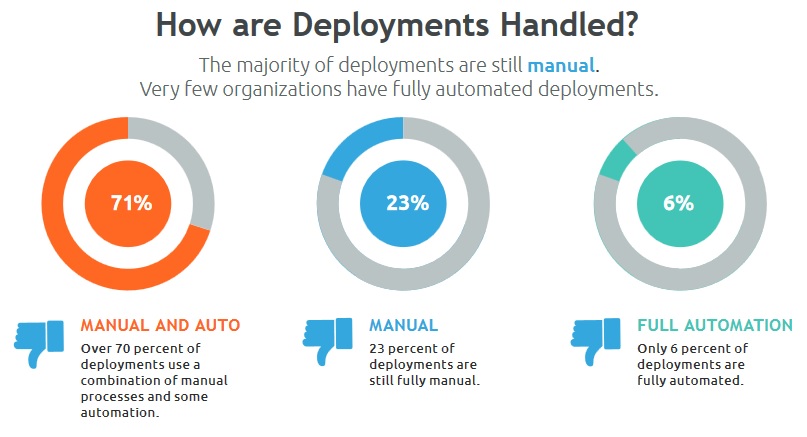
It Gets Worse
The two remaining datasets from this section tells us perhaps the most disappointing fact – 23 percent of deployments are still fully manual and only 6 percent of deployments are fully automated. Let’s face it; manual intervention often leads to errors and non-repeatable processes. No bueno. If testing or deployments are handled manually, it’s nearly impossible to implement continuous delivery or continuous integration in any way. What this statistic tells us is that many don’t realize that they have increased the risk of defects to their software (which almost always creates unplanned workloads), or a higher risk of deployments failing all together.
When relying on manual processes versus automation, an entire host of problems can emerge. The top challenges with manual deployments are:
1. Environment differences and configuration drift
2. Manual, error-prone steps
3. Complex application dependencies
4. Manual deployments often lead to more time spent troubleshooting deployment failures
The bottom line is this: manual deployments are extremely brittle and error-prone. This creates not only failed deployments, but also the loss of hundreds of worker hours trying to troubleshoot those failures. This is certainly painful in mission critical production environments, but carries great cost, even long before you reach production release.

The Bigger Truth
As surprising as it might be to read in 2017, IT departments are still struggling to release software at the rate the business demands. As we see from the Puppet and DORA 2016 State of the DevOps Report, automation eliminates common challenges that come with manual deployments, and delivers better results.
Deployment automation is the linchpin of DevOps success. Automated deployments allow organizations to drastically cut cycle times, accelerate releases and reduce application backlogs. Specifically, according to the Puppet and DORA Report, automation provides 200x more frequent deployments, 3x lower change failure rates, 24x faster recovery from failures and 2555x shorter lead times.

Deployment Automation is the Linchpin of DevOps Success
DevOps is not the responsibility of one person or one team. It’s a company mindset that when set in motion, delivers immediate value. The right Application Release Automation solution can dramatically accelerate your time-to-market and cycle times, give you confidence in your IT operations, enhance teamwork, and reduce operational costs.
Industry News
JFrog is partnering with Hugging Face, host of a repository of public machine learning (ML) models — the Hugging Face Hub — designed to achieve more robust security scans and analysis forevery ML model in their library.
Copado launched DevOps Automation Agent on Salesforce's AgentExchange, a global ecosystem marketplace powered by AppExchange for leading partners building new third-party agents and agent actions for Agentforce.
Harness completed its merger with Traceable, effective March 4, 2025.
JFrog released JFrog ML, an MLOps solution as part of the JFrog Platform designed to enable development teams, data scientists and ML engineers to quickly develop and deploy enterprise-ready AI applications at scale.
Progress announced the addition of Web Application Firewall (WAF) functionality to Progress® MOVEit® Cloud managed file transfer (MFT) solution.
Couchbase launched Couchbase Edge Server, an offline-first, lightweight database server and sync solution designed to provide low latency data access, consolidation, storage and processing for applications in resource-constrained edge environments.
Sonatype announced end-to-end AI Software Composition Analysis (AI SCA) capabilities that enable enterprises to harness the full potential of AI.
Aviatrix® announced the launch of the Aviatrix Kubernetes Firewall.
ScaleOps announced the general availability of their Pod Placement feature, a solution that helps companies manage Kubernetes infrastructure.
Cloudsmith raised a $23 million Series B funding round led by TCV, with participation from Insight Partners and existing investors.
IBM has completed its acquisition of HashiCorp, whose products automate and secure the infrastructure that underpins hybrid cloud applications and generative AI.
Veeam® Software announces Veeam Kasten for Kubernetes v7.5, designed to deliver Kubernetes-native data resilience for enterprises.
DeepSource released Globstar, an open-source project bringing code security tooling to the AppSec community, with no restrictions on commercial usage.
Google Cloud announced the public preview of Gemini Code Assist for individuals, a free version of Gemini Code Assist that will give students an easy-to-use free AI coding assistant with the highest usage limits available














