Check Point® Software Technologies Ltd.(link is external) has emerged as a leading player in Attack Surface Management (ASM) with its acquisition of Cyberint, as highlighted in the recent GigaOm Radar report.
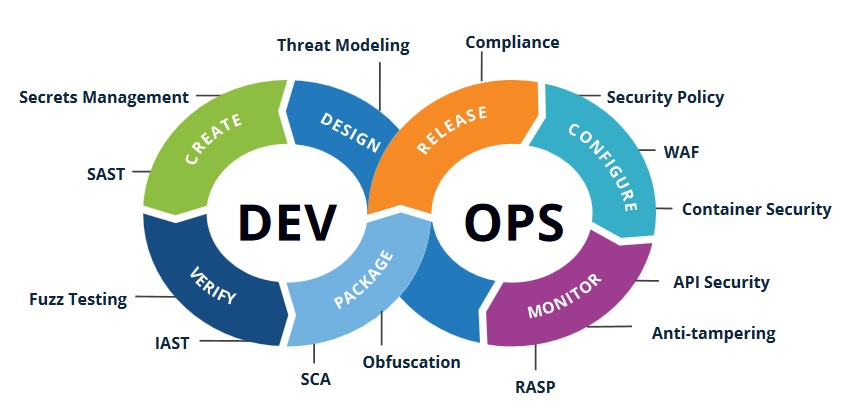
As the volume, development velocity, and variety of applications and their attack vectors skyrocket, it's time to rethink how we use application hardening. Application hardening, also known as "application shielding" and "in-app protection," protects live applications from reverse engineering and tampering.
Application hardening isn't just for mobile applications anymore but is emerging as a standard way of protecting desktop and web applications across industries and for a good reason. Bringing application hardening into a comprehensive DevSecOps strategy will help enterprises overcome secure coding skills gaps and better enable developer teams to deliver higher quality applications faster to meet the demands of today's environment.
By 2025, IDC predicts that 750 million discrete applications will be released worldwide, up from roughly 195 million in 2021 (The Need for Application Hardening as Part of a Holistic DevSecOps Strategy, May 2023). With more applications being accessed from the growing variety of devices and platforms, the attack surface continues to expand. At the same time, cybercriminals keep finding new ways to exploit vulnerabilities, even in securely coded applications via reverse engineering and tampering techniques.
Unsurprisingly, application development velocity keeps increasing, given the popularity of DevOps practices and innovative developer tools powered by automation and AI to speed up dev cycles. IDC expects 70% of large organizations will have the means to release daily code in production by 2025, up from a meager 5% in 2021.
Now companies are integrating DevSecOps technologies with DevOps processes to make security best practices part of the developer's responsibilities. In reality, many developers need more secure coding experience and help to keep up with the shifting threat landscape. Application hardening helps fill these gaps.
Source: IDC, 2023(link is external)
The following are benefits of application hardening as part of DevSecOps
Improved build-time security posture without burdening developers
Code obfuscation is the most common type of build-time application hardening. It is the process of making code difficult for humans or machines to understand while retaining the integrity and behavior of the application. This process can be automated so more secure applications are released without requiring developers to be security experts. The best obfuscation solutions are regularly updating and releasing new techniques to prevent deobfuscation and reverse engineering.
Visibility into potential attacks of applications in production
Application tampering is the unsanctioned use of an application in a way not intended or authorized by the organization. Tampering happens after an application is released, and unless production monitoring is in place, the organization cannot detect it. Tampering is a growing problem that has led to data breaches, financial and reputational losses, and legal liabilities.
Tampering detection uncovers application and user behavior that signals an application is being messed with. For instance, a threat actor could use a debugger to reverse engineer an application for malicious intent. Device fingerprinting can provide insight into how a user connects to an application to understand behavior better. When alerted to tampering, enterprises receive detailed visibility into information such as the device, operating system, browser, IP address, and geographic location.
Real-time mitigation of attacks from known and unknown threats
While Web application firewalls (WAF) are used to protect Internet-based applications, they analyze the traffic to and from an application but are blind to data within applications. According to Kaspersky, public-facing web apps are the leading attack vector cybercriminals use to penetrate an organization's perimeter.
Application hardening should be integrated into DevOps workflows. Enterprises that take this approach can ensure that nonhardened applications are not released without security protections — for example, through coordination of release orchestration with an Open Policy Agent (OPA).
Application hardening also needs to encompass application monitoring and runtime application self-protection (RASP), which enables applications to detect tampering and automatically respond if tampering is detected. RASP security offers real-time threat detection by looking at both the application and analyzing the context of events causing the current behavior of the application. With this visibility into an application's logic and data flow, RASP can trigger automatic, customizable actions in response to unexpected behavior, offering greater attack protection of applications in production.
When considering an application hardening solution, enterprises should identify solutions that incorporate tamper detections, code obfuscations, and RASP with customizable event responses. Additionally, any solution should integrate with DevOps and DevSecOps workflows and allow for proper governance and compliance checks. Finally, solutions that are open-architecture and allow for heterogeneous toolsets will provide the most flexibility as they are incorporated into workflows.
Industry News
GitHub announced the general availability of security campaigns with Copilot Autofix to help security and developer teams rapidly reduce security debt across their entire codebase.
DX and Spotify announced a partnership to help engineering organizations achieve higher returns on investment and business impact from their Spotify Portal for Backstage implementation.
Appfire announced its launch of the Appfire Cloud Advantage Alliance.
Salt Security announced API integrations with the CrowdStrike Falcon® platform to enhance and accelerate API discovery, posture governance and threat protection.
Lucid Software has acquired airfocus, an AI-powered product management and roadmapping platform designed to help teams prioritize and build the right products faster.
StackGen has partnered with Google Cloud Platform (GCP) to bring its platform to the Google Cloud Marketplace.
Tricentis announced its spring release of new cloud capabilities for the company’s AI-powered, model-based test automation solution, Tricentis Tosca.
Lucid Software has acquired airfocus, an AI-powered product management and roadmapping platform designed to help teams prioritize and build the right products faster.
AutonomyAI announced its launch from stealth with $4 million in pre-seed funding.
Kong announced the launch of the latest version of Kong AI Gateway, which introduces new features to provide the AI security and governance guardrails needed to make GenAI and Agentic AI production-ready.
Traefik Labs announced significant enhancements to its AI Gateway platform along with new developer tools designed to streamline enterprise AI adoption and API development.
Zencoder released its next-generation AI coding and unit testing agents, designed to accelerate software development for professional engineers.
Windsurf (formerly Codeium) and Netlify announced a new technology partnership that brings seamless, one-click deployment directly into the developer's integrated development environment (IDE.)













